Sometimes, you want to access a secret stored in Account A from a resource running in Account B. For example, an EC2 instance or Lambda function in Account B wants to read database credentials or API keys saved in AWS Secrets Manager of Account A.
This guide shows how to do that securely using AWS best practices.
📁 Setup Overview
- Account A (Destination): Owns the secret in AWS Secrets Manager
- Account B (Source): Has the EC2 or Lambda that needs to access the secret
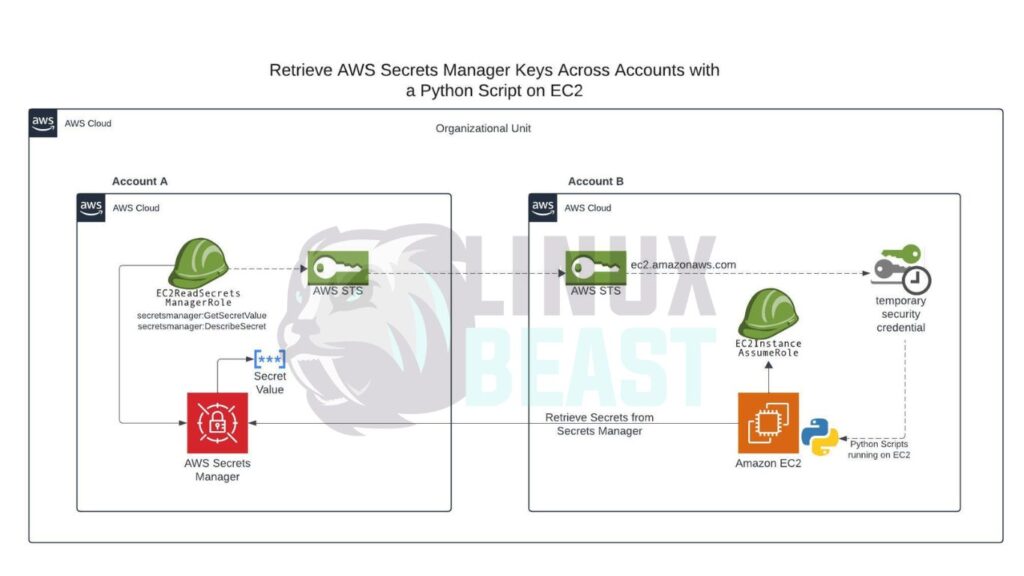
✅ Step 1: Configure Secrets Manager Policy in Account A
Create a resource-based policy on the secret to allow Account B’s IAM role to read it. You can also restrict access by AWS Organization ID for better control:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": "*",
"Action": "secretsmanager:GetSecretValue",
"Resource": "arn:aws:secretsmanager:REGION:ACCOUNT_A_ID:secret:YOUR_SECRET_NAME",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"aws:PrincipalOrgID": "o-s3xxxxx"
}
}
}
]
}📌 Make sure to replace:
REGIONACCOUNT_A_IDYOUR_SECRET_NAMEo-s3xxxxxwith your actual Organization ID
🔑 Step 2: Grant KMS Key Access in Account A
If your secret is encrypted using a customer-managed KMS key, you must also update its policy:
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::ACCOUNT_B_ID:role/ROLE_NAME_IN_B"
},
"Action": [
"kms:Decrypt",
"kms:DescribeKey"
],
"Resource": "*"
}🛡️ Step 3: (Optional) Create IAM Role in Account A (Secure Method)
Instead of using direct resource policy access, you can create a role in Account A that Account B can assume. This allows better control and audit.
Trust Policy (for the role in Account A):
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::ACCOUNT_B_ID:role/ROLE_NAME_IN_B"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}Permissions Policy (attached to role in Account A):
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"secretsmanager:GetSecretValue",
"secretsmanager:DescribeSecret",
"kms:Decrypt"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:secretsmanager:REGION:ACCOUNT_A_ID:secret:YOUR_SECRET_NAME",
"arn:aws:kms:REGION:ACCOUNT_A_ID:key/YOUR_KEY_ID"
]
}🪰 Step 4: Set IAM Role in Account B (Where EC2 or Lambda Runs)
Trust Policy for EC2 Role:
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "ec2.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}Permissions Policy:
If you’re using the IAM Role in Account A method:
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Resource": "arn:aws:iam::ACCOUNT_A_ID:role/ReadSecretCrossAccountRole"
}🐍 Step 5: Use Python to Retrieve the Secret
Here’s a simple Python script that assumes the role and reads the secret:
import boto3
import os
def assume_role(role_arn):
sts_client = boto3.client('sts')
assumed = sts_client.assume_role(
RoleArn=role_arn,
RoleSessionName='crossaccount-session'
)
creds = assumed['Credentials']
return creds
def get_secret(secret_name, creds):
session = boto3.session.Session(
aws_access_key_id=creds['AccessKeyId'],
aws_secret_access_key=creds['SecretAccessKey'],
aws_session_token=creds['SessionToken']
)
client = session.client('secretsmanager')
response = client.get_secret_value(SecretId=secret_name)
return response['SecretString']
if __name__ == '__main__':
ROLE_ARN = os.environ['ROLE_ARN']
SECRET_NAME = os.environ['SECRET_NAME']
try:
creds = assume_role(ROLE_ARN)
secret = get_secret(SECRET_NAME, creds)
print("Secret:", secret)
except Exception as e:
print("Error:", str(e))
Set your environment variables:
export ROLE_ARN=arn:aws:iam::ACCOUNT_A_ID:role/ReadSecretCrossAccountRole export SECRET_NAME=YOUR_SECRET_NAME
✅ Conclusion
- Use Secrets Manager resource policy to allow access
- Grant KMS key permission if you use a custom key
- Use IAM AssumeRole for secure cross-account access
- You can further secure access using
aws:PrincipalOrgIDcondition

